Convessità e direzionalità
Un insieme connesso S di celle può essere:
- orizzontalmente convesso se date due sue celle qualsiasi sulla stessa linea orizzontale, tutte le celle comprese, in orizzontale, tra queste due appartengono a S;
- verticalmente convesso se date due sue celle qualsiasi sulla stessa linea verticale, tutte le celle comprese, in verticale, tra queste due appartengono a S;
- diagonalmente convesso;
- orientato a Nord-Est (o orientato, in breve) se contiene un punto v0, detto sorgente, tale che ogni altro punto di A può essere raggiunto da v0 da un cammino composto da passi unitari Nord ed Est;
- orientato a NO, SE, SO ma anche NEO, SEO, NSE, NSO.
def generaSENW(n,tipo):
S = {(0,0)}
tipi = {"N":(0,1), "O":(-1,0), "S": (0,-1), "E":(1,0)}
B = {tipi[t] for t in tipo}
for i in range(n-1):
(x,y) = random.choice(tuple(B))
S.add((x,y))
B.remove((x,y))
B = B | {(x+tipi[t][0],y+tipi[t][1]) for t in tipo}-S
return S
plot_S(generaSENW(10,"NE"))
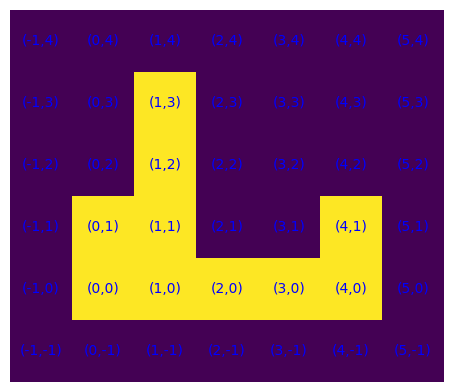
def is_Vconv(S):
lst_x = [x for x,_ in S]
for x in lst_x:
S_x = [y for (x_,y) in S if x_ == x]
if len(S_x) -1 != max(S_x)-min(S_x):
return False
return True
def is_Oconv(S):
lst_y = [y for _,y in S]
for y in lst_y:
S_y = [x for (x,y_) in S if y_== y]
if len(S_y) -1 != max(S_y)-min(S_y):
return False
return True
def is_Dconv(S, diag="+"):
diag = {}
for (x, y) in S:
d = x + y if diag=="+" else x - y
diag.setdefault(d, []).append((x, y))
for k, Sd in diag.items():
coords = [x for x, y in Sd]
min_c, max_c = min(coords), max(coords)
if max_c - min_c + 1 != len(coords):
return False
return True
S, _ = genera(20)
plot_S(S)
is_Vconv(S), is_Oconv(S), is_Dconv(S)
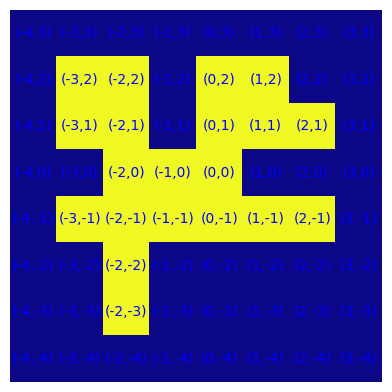
(False, False, False)
Un polimino può avere, tra queste, più proprietà. Ad esempio si dice:
- convesso un polimino convesso sia per colonna che per riga,
- a scala un polimino orientato verso NE o SO,
- istogramma a barre, convessi per colonna orientati verso NE e NO,
- stack, un istogramma a barre convesso per riga,
- partizione, o anche diagramma di Ferrers, polimini orientati verso NE, NO e SE.
Si osservi che il rettangolo involuco di un polimino $S$ ha vertici opposti $(\min\{x, (x,y)\in S\}, \min\{y, (x,y)\in S\}),\; (\max\{x, (x,y)\in S\}, \max\{y, (x,y)\in S\})$.
def box(S):
return {(x, y) for x in range(min(x for (x,y) in S), max(x for (x,y) in S) + 1)
for y in range(min(y for (x,y) in S), max(y for (x,y) in S) + 1)}
Invece il polimino involuco convesso di un polimino si può ottenere nel modo seguente.
def invConv(S):
C = set()
for x0 in {x for (x,y) in S}:
ym, yM = min([y for (x,y) in S if x==x0]), max([y for (x,y) in S if x==x0])
for y in range(ym,yM+1):
C.add((x0,y))
for y0 in {y for (x,y) in S}:
xm, xM = min([x for (x,y) in S if y==y0]), max([x for (x,y) in S if y==y0])
for x in range(xm,xM+1):
C.add((x,y0))
return C
o anche
def invConv(S):
lst_x,lst_y = zip(*S)
xM, xm = max(lst_x), min(lst_x)
yM, ym = max(lst_y), min(lst_y)
return {(x, y) for x in range(xm, xM + 1)
for y in range(min(y for (t,y) in S if t==x ), max(y for (t,y) in S if t==x ) + 1)
} | {(x, y) for y in range(ym, yM + 1)
for x in range(min(x for (x,t) in S if t==y ), max(x for (x,t) in S if t==y ) + 1)
}
Per approfondimenti:
- Partizioni Piane: Funzione Generatrice e Formula Ricorsiva, Tesi di Laurea di Luca Bartoli